
India is often referred to as the ‘Diabetes Capital of the World’, as it accounts for 17% per cent of the total number of diabetes patients in the world. More than 50% of people are unaware of their diabetic status which leads to health complications. If not detected or treated early, it can cause blindness, kidney failure, heart attack or stroke among other problems.
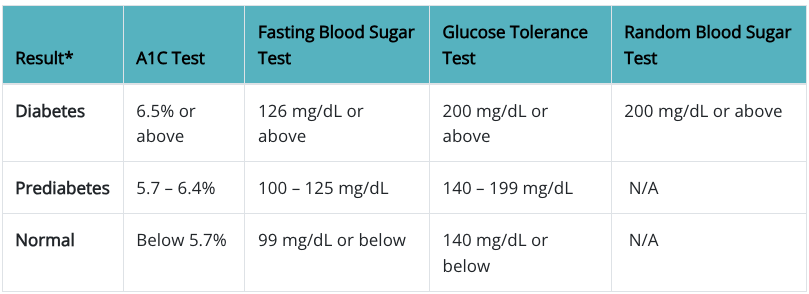
Glucose is an important energy source for our brain, muscles and tissues to perform daily functions. Insulin helps manage its absorption. Diabetes is a condition that happens when your blood sugar (glucose) is higher than required.*(See the range below)
It develops when your pancreas does not make enough insulin or any at all, or when your body is not responding properly to the effects of insulin. Diabetes affects people of all ages. Most forms of diabetes are chronic (lifelong), and all forms are manageable with regular monitoring, medications and lifestyle changes.
Diabetes is of different types with short-term and long-term implications for treatment:
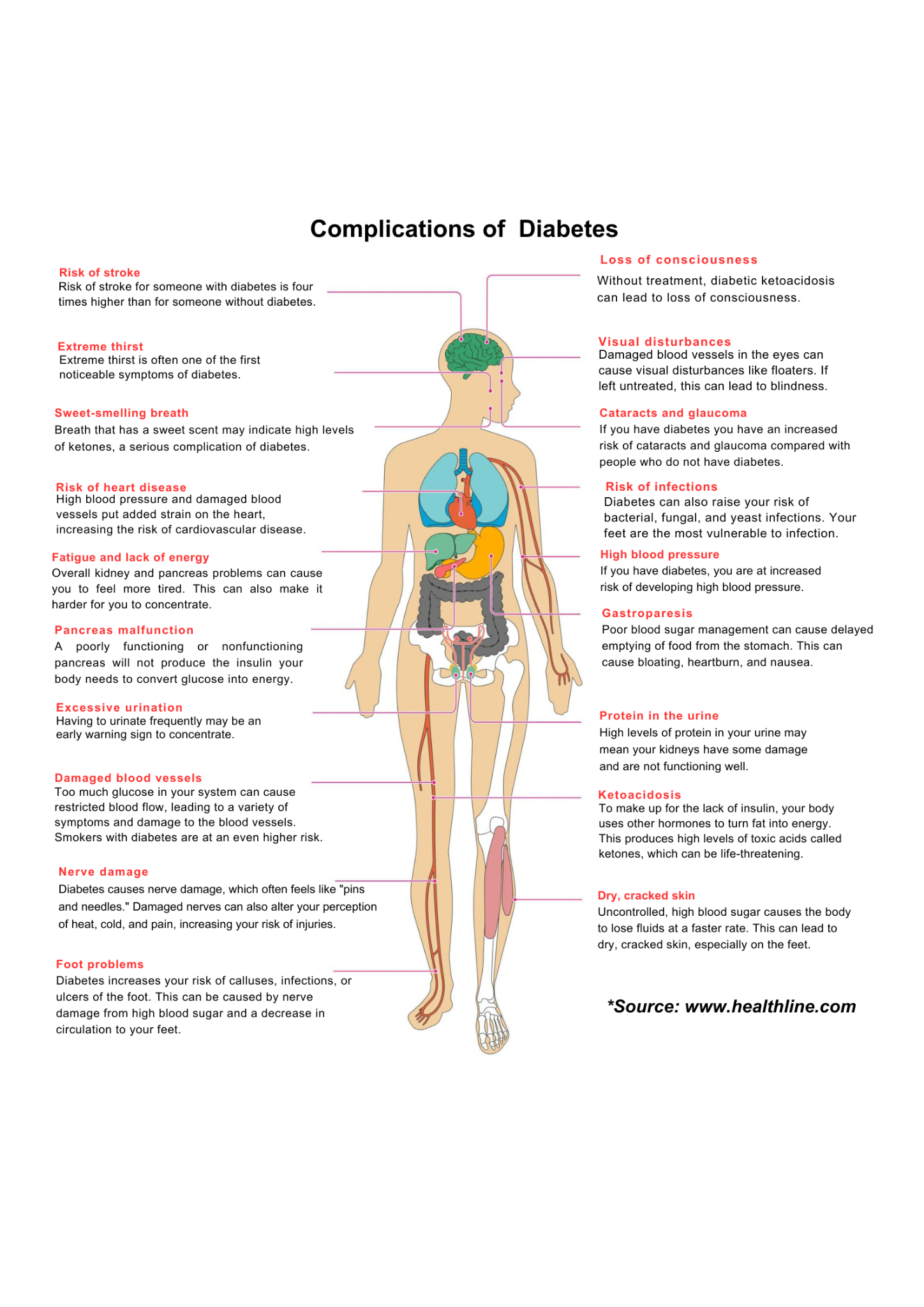
Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually and may be disabling or even life-threatening. The longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications: Heart attack, stroke, Kidney damage, Eye problems, Foot problems, infections or slow wound healing, Sexual dysfunction, Mental health issues etc.
Diabetes symptoms depend on how high your blood sugar is. People with prediabetes, gestational diabetes or type 2 diabetes, may not have any symptoms at all or you may not notice them since they develop slowly. Measuring your diabetes is the only way to know whether you have it or not. In type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly and be more severe. Common symptoms of diabetes.

Factors that increase the risk for diabetes include having a family history of a parent or sibling with diabetes, gestational diabetes, prediabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and being physically inactive or obese/overweight. Both men & women can get diabetes, adults above 45 are more likely to be affected however the incidence is among people between 20-45 years of age.
Diabetes can be checked by blood tests. Tests for type 1 and type 2 diabetes and prediabetes:
Depending on what type of diabetes you have, the doctor can prescribe a combination of medications, insulin and lifestyle changes for your treatment. Do not self-medicate or adjust the insulin doses independently. Follow professional advice always.
Medication: Seek your doctor's advice for a comprehensive treatment plan. A variety of medicines is available, however, the doctor will customise the salt, doses, and timings of intake, to suit the patient's overall condition. Remember to inform the doctor of other medications that you normally take. Do not self-medicate, miss or adjust doses independently. Never copy or try medicines that your friends or family members take. Keep sufficient stock of your diabetes medicines handy at all times especially while travelling. If diabetes is unchecked for a long time it can result in serious consequences.
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells. Insulin can not be taken orally.
You can not prevent Type 1- autoimmune and genetic forms of diabetes as of the data available yet. But you can prevent and manage Prediabetes & Type 2 diabetes even if it runs in your family with these lifestyle changes:
Regular monitoring of diabetes is a must for treatment. You can monitor your blood sugar level with a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Early detection, proper management, and a proactive lifestyle can make a significant difference in effectively handling diabetes.