
Heart Attack: How to Detect and Respond
What is it:
Heart attack is a serious medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually due to a blood clot. This blockage prevents oxygen from reaching the heart muscles and, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications or even death. This is why a heart attack needs to be rushed into immediate intervention to resolve the obstruction and restore blood flow. Recognizing the signs and taking quick action can significantly increase the chances of survival and reduce long-term damage to the heart.
Symptoms of Heart Attack:
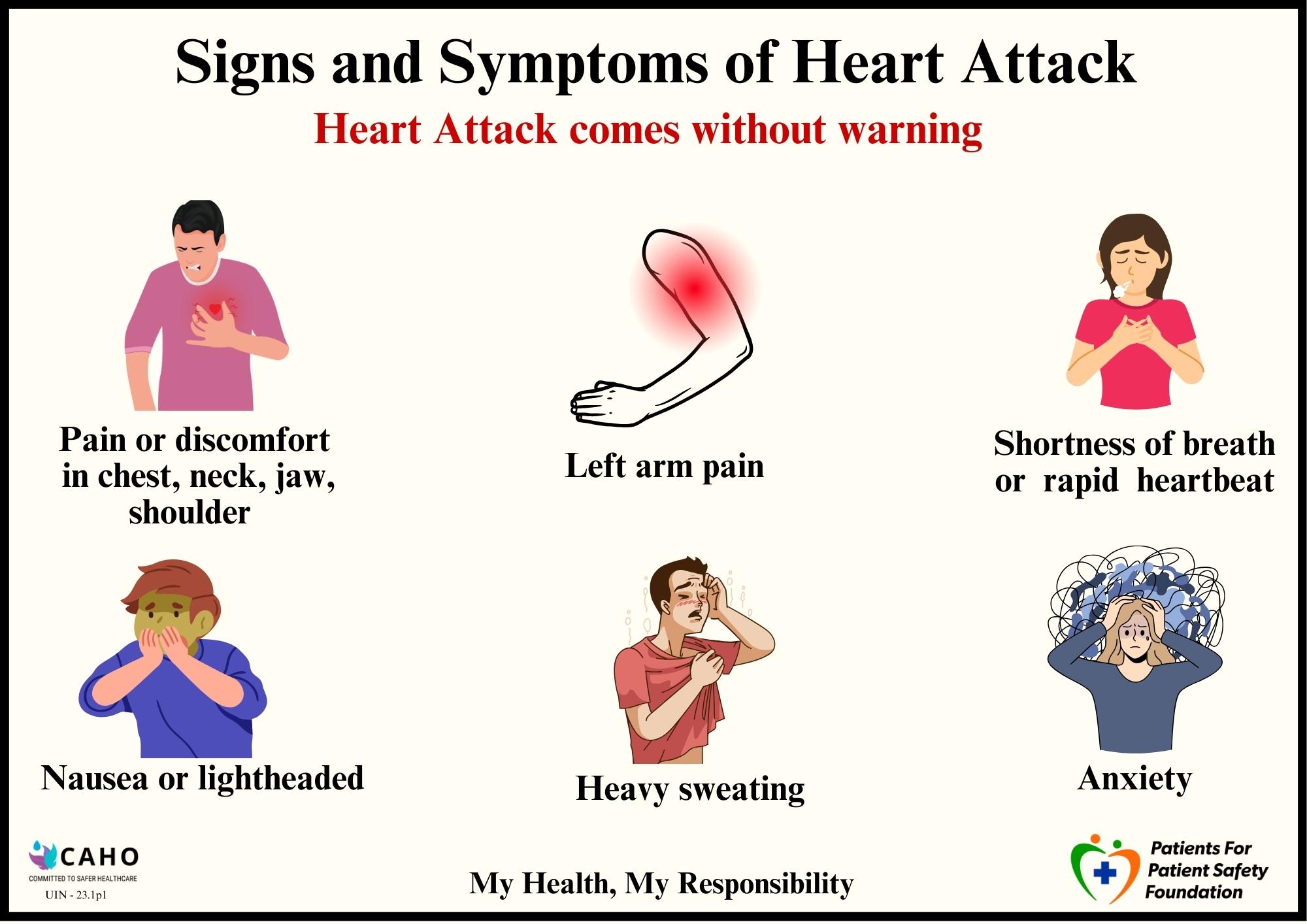
Often a heart issue is mistaken as heartburn or gastric issues and delay could lead to serious consequences and delayed treatment.
Who is at Risk:
A heart attack can happen to anyone, however, certain factors can increase your risk. You may be at a higher risk for a heart attack if you
- Have diabetes and suffer from high blood pressure or high cholesterol
- Are obese or overweight
- Smoke or are exposed to secondhand smoke
- Experience significant stress on a regular basis
- No physical activity
- Have a family history of heart disease
Possible Complications of a Heart Attack:
- Damage to the heart or heart valves
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Another heart attack
- Heart failure because the heart doesn't pump as well as it once did
- Shock and other organ failure
- Death
What to do if you feel you are having a Heart Attack:
- Inform someone nearby immediately
- Open the front door if alone
- Rest and try to stay as calm as possible. Stress and panic can worsen the situation.
- Chew aspirin if you are not allergic to it and your doctor has not advised against its use.
- Call your doctor, share symptoms, and take advice.
- Do not drive yourself. Ask for a Cardiac Ambulance. Dial 102. If delayed, have a neighbor or friend drive you to the nearest hospital that has MRI and CT scan facilities.
Guide on how to help someone experiencing a Heart Attack:
- Stay calm. Try to keep the person calm. Stress can worsen the situation. Help the person sit down and make them as comfortable as possible.
- Call a physician for advice.
- If the person is not allergic to aspirin, have them chew one regular-strength.
- Perform CPR If the person becomes unresponsive and stops breathing, you may need to perform CPR if you are trained to do so.
- Call for a Cardiac Ambulance (102). If delayed, drive the patient to the nearest hospital with MRI and CT scan facilities.
Remember, time is crucial during a heart attack. Seek emergency care immediately for the best outcome. If you are at risk, discuss the signs and symptoms with your healthcare provider to be prepared for emergencies.
How is a Heart Attack Diagnosed:
- Imaging tests
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Blood tests
- Echocardiography (Sonography)
How is a Heart Attack Treated:
The main goals of heart attack treatment are to restore blood flow to the affected heart muscle as soon as possible and minimize damage to the heart. Treatment typically involves:
- Medications like aspirin to stop blood clotting. Other medicines are also given during or after a heart attack to help the heart work.
- Surgical and other procedures may be done in rare cases to open a blocked artery.
Prompt treatment and lifestyle changes are crucial for minimizing heart damage and preventing complications after a heart attack.
Preventive Measures:
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet
- Managing stress
- Quitting smoking and alcohol intake
- Taking prescribed medications
- Regular heart health check-ups
By adopting these healthy habits and managing risk factors, you can reduce your chances of having a heart attack and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
 Back
Back