Gallbladder Stones: A Hidden Hazard
What are Gallbladder Stones:
The gallbladder is a small storage tank for bile, a liquid that helps your body
digest fats. Sometimes, substances in bile, like cholesterol and bilirubin, can
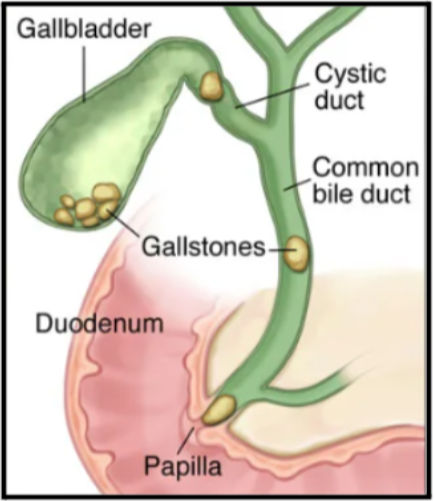
become concentrated and form small, hard lumps. These are called gallstones.
They can range in size from a grain of sand to a table tennis ball.
Why Do They Happen:
It is not clearly known why gallstones form, but several factors contribute:
- Too much cholesterol in your bile can crystallise and form stones.
- Too much bilirubin in your bile due to conditions like liver cirrhosis or
blood disorders can cause the formation of stones.
- Poor emptying of the gallbladder, the bile becomes too concentrated,
leading to gallstone formation.
Consequences of Gallbladder Stones:
Many people have gallstones and never experience any problems. These are
often called "silent gallstones." However, if a gallstone blocks one of the ducts
leading from your gallbladder, it can cause various issues that need immediate
attention.
- Gallbladder attack: A sudden and intense pain in the upper right part of
your abdomen, often after eating fatty foods. It can last for several hours.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder/pancreas: A gallstone blocking the
duct for too long can cause the gallbladder or pancreas to become
inflamed and infected.
- Inflammation of the bile ducts: If a gallstone blocks the main bile duct,
it can lead to infection and inflammation of the bile ducts.
In some cases, gallstones can cause jaundice as well.
What Are the Symptoms:
Latent gallstones do not have symptoms; however, if they become large or
move into the ducts, there could be symptoms.
- Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your
abdomen
- Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the centre of your abdomen, just
below your breastbone
- Back pain between your shoulder blades or in your right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
These attacks can happen at any time, and more often after a fatty meal or at
night. If you experience these symptoms, see a doctor immediately
Diagnosis of Gallstones:
Based on your symptoms and clinical review, the doctor may recommend:
- Abdominal ultrasound: The most common test, as it can clearly show
gallstones.
- CT scan or MRI: These imaging tests can provide more detailed pictures
of your abdomen/position of the stones.
- Blood tests: To check for signs of infection, inflammation, or jaundice.
How are They Treated:
Gallstones do not go away on their own. If they have been detected or you are
experiencing pain or complications, your doctor might recommend:
- Surgery to remove the gallbladder is the most common and effective
treatment, as it is not easy to remove stones otherwise. It is often
performed laparoscopically. The good news is you can live a normal,
healthy life without your gallbladder if you take certain dietary
precautions.
- Medications to dissolve gallstones: For certain cholesterol gallstones,
medications may be prescribed, which can take months or years, and
gallstones may recur if the medication is stopped.
- Endoscopic procedures: Used to remove gallstones that have moved
into the bile ducts.
Is There a Way to Detect Them Early:
Let it not become an emergency. Early detection through imaging tests, often
part of annual Preventive Health Check-ups, can detect "silent" gallstones
before they cause problems. Regular check-ups and body awareness can help. If
you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially recurrent
abdominal pain, it is important to see your doctor promptly.