
Osteoporosis - Prevention, Symptoms, Test and Treatment
Introduction
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that develops when bone density and bone mass decrease or when the structure and strength of bone change. This can lead to a decrease in bone strength that increases the risk of fractures (broken bones). Other symptoms include back pain, change in natural posture, and shortness of breath. It is a silent disease because you may not know you have this condition until you break a bone including the hips, wrist or spine. Prioritizing bone health through regular screenings, exercise vitamin supplements as prescribed by the doctor, and adopting a bone-friendly lifestyle can mitigate the impact of osteoporosis.
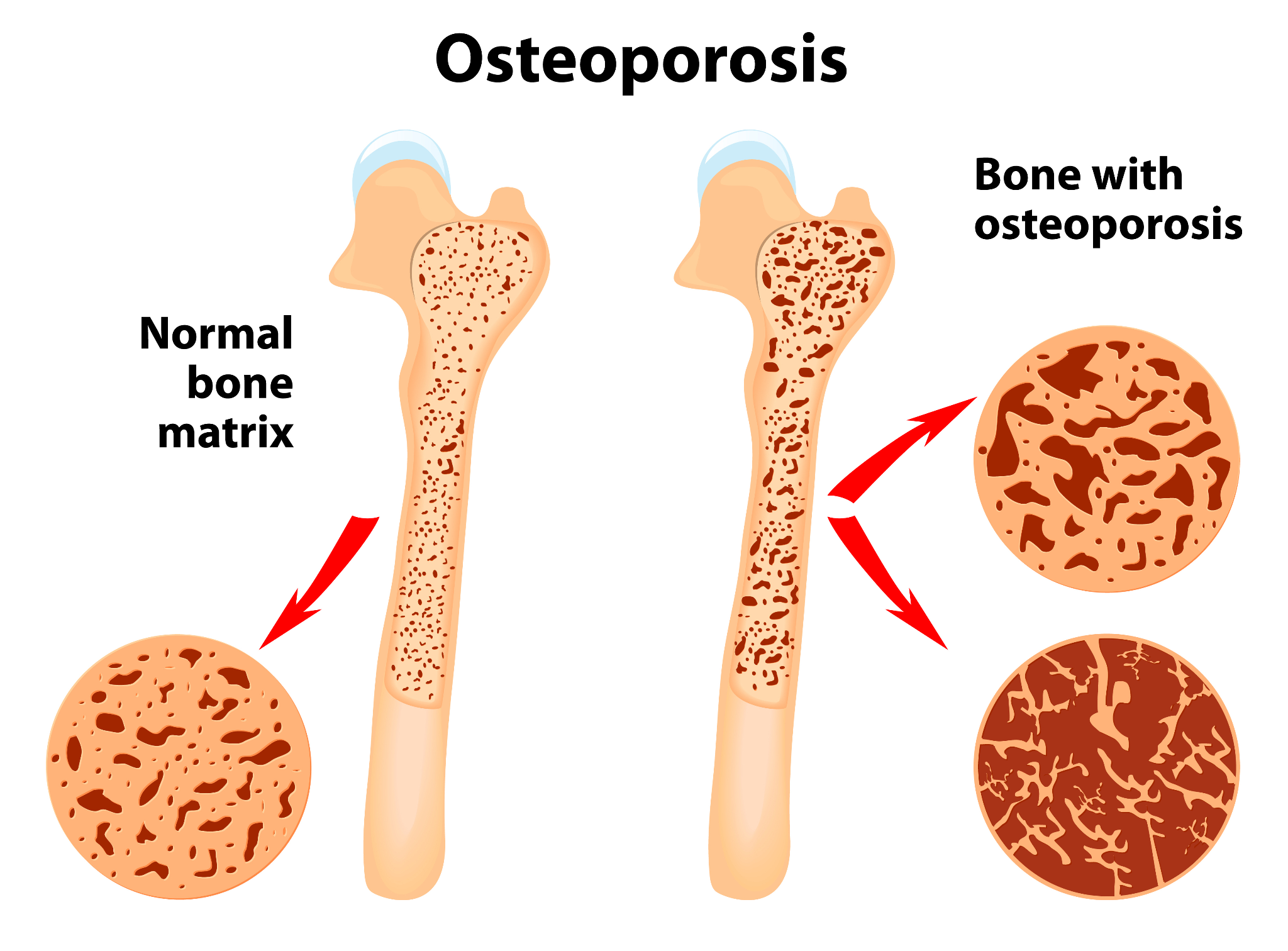
Why are women more susceptible to Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis affects more women than men. due to hormonal changes, specifically the decline in estrogen levels during menopause after, the age of 50, there is a significant reduction in estrogen production. This hormonal shift accelerates bone loss, leading to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures Additionally, women generally start with lower bone density than men, and their smaller bone size contributes to a faster decline in bone health as they age.
Signs and symptoms of Osteoporosis:
The symptoms effects of Osteoporosis are outseen early and felt when incidents happen
- Back pain, caused by a broken or collapsed bone in the spine,
- Bone that breaks much more easily than expected
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped posture or changes in your natural posture like bending forward.
- Shortness of breath (if disks in your spine are compressed enough to reduce your lung capacity)
Who is at risk for Osteoporosis:
- Age: As women grow older, especially postmenopausal women with declining estrogen levels,
- Body frame size: Women who have small body frames tend to have a higher risk because they might have less bone mass to draw from as they age
- Low calcium intake: Not getting enough calcium or vitamin D in your diet and not getting enough physical exercise
- Family history: Having a parent or sibling with osteoporosis puts you at greater risk, especially if your mother or father fractured a hip.
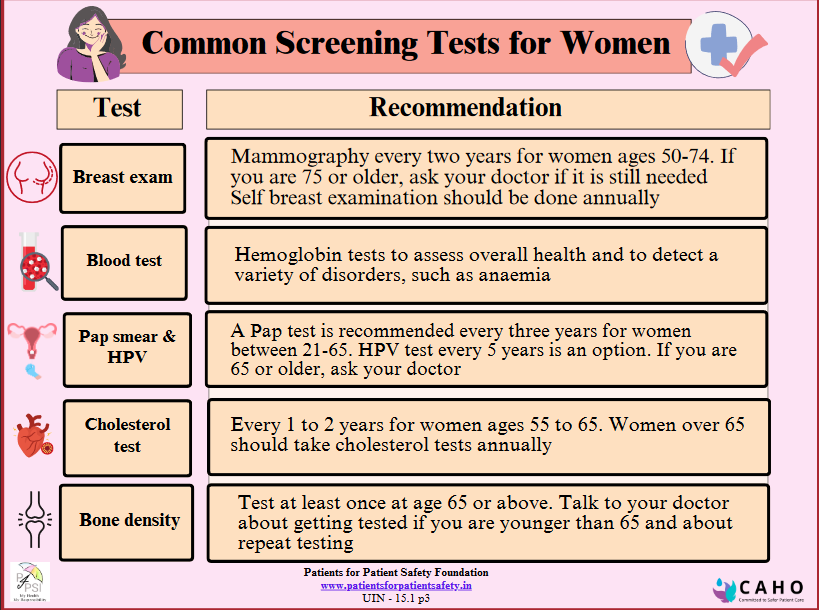
How is Osteoporosis diagnosed:
A healthcare provider will diagnose osteoporosis with:
- Bone density test is a special imaging test that shows the density of your bones ‘
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) Scan: It uses low-dose X-rays to scan specific bones, usually the spine, hip or forearm, and provides a T-score that compares bone density to that of a healthy young adult.
Treatment of Osteoporosis:
Your healthcare provider will suggest a combination of treatments that slow down your bone loss and strengthen your existing bone tissue.
Exercise: Regular exercise can strengthen and support your bones (and all the tissue connected to them, like your muscles, tendons and ligaments). Your doctor might suggest weight-bearing exercises to strengthen your muscles and train your balance.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements: Your doctor will prescribe prescription calcium or vitamin D supplements. Most of them are available including dosage and over the counter.
- Medications for osteoporosis: In some cases, you may be prescribed
Prevention for Osteoporosis:
- Ensure a sufficient daily intake of calcium, a crucial mineral for bone health. Good dietary sources include dairy products, leafy green vegetables and nuts.
- Maintain adequate levels of vitamin D, which helps the body absorb calcium. fatty fish and fortified foods are sources of vitamin D.
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging and resistance training. These activities stimulate bone formation and help maintain bone density.
- Preventing falls at home
Precautions in case you have Osteoporosis:
Ensure living space is well-lit and free of tripping hazards, use handrails on stairs and in bathrooms. Wear supportive, non-slip footwear. Engage in regular exercises that improve balance and strength and maintain a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone strength. Read more on Preventing falls at home
 Back
Back