
Female Fertility - Symptoms, Detection and Treatment
Introduction
Female fertility relates to the health and function of the reproductive organs. the capacity of female reproductive system to release viable eggs and the ability to support a fertilised egg and carry the pregnancy to the full term. Factors that adversely affect fertility include certain lifestyles such as excess smoking, alcohol intake, genetics, comorbidities and other environmental factors. Embracing a healthy lifestyle not only promotes overall well-being but also serves as a measure to optimise fertility.
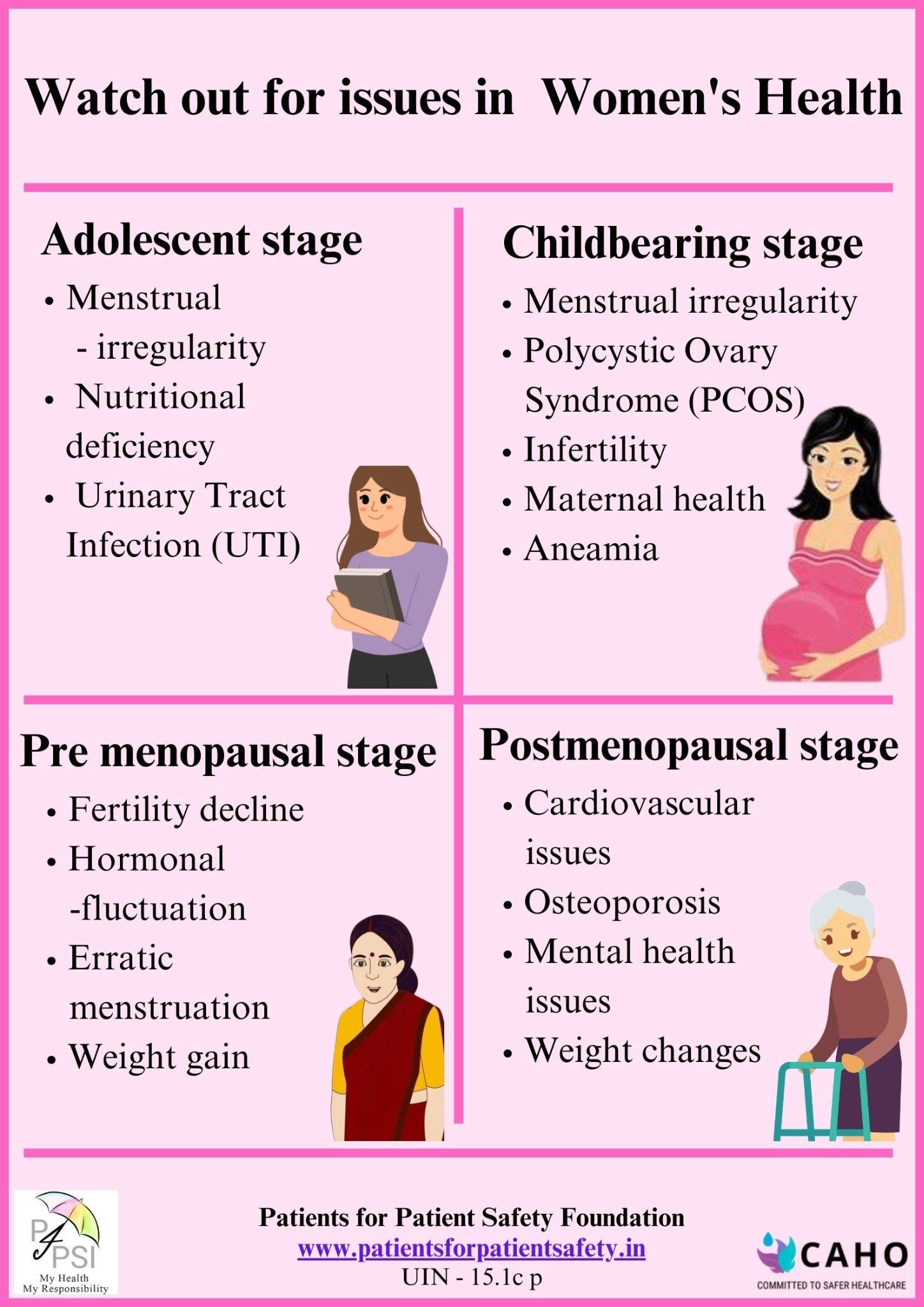
Common signs and symptoms of fertility issues:
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Unusually light or heavy bleeding and bad menstrual cramps or pelvic pain
- Recurrent miscarriage
Possible causes of fertility issues:
- Ovulatory disorders: Irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation, often associated with conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), can hinder conception.
- Uterine issues: Structural abnormalities in the uterus, such as fibroids (non-cancerous growths) or uterine polyps, can impact fertility by affecting implantation or interfering with the menstrual cycle.
- Hormonal imbalance: Irregularities in hormonal levels, including those related to the thyroid or reproductive hormones, can affect ovulation and the overall reproductive process.
- Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI): The early depletion of ovarian follicles, leading to decreased egg production and ovarian function, can result in fertility issues.
- Genetic factors: Certain conditions may affect reproductive organs or impact the quality of eggs, contributing to fertility challenges.
- Weight: Both underweight and overweight conditions can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting ovulation and fertility.
- Age-related factors: As women age, the quantity and quality of eggs naturally decline, leading to reduced fertility, increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities and a higher chance of miscarriage.
- Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use and high levels of stress can contribute to fertility problems.
How is infertility diagnosed and tested:
The diagnosis of infertility may involve medical assessments and tests such as:
- Pelvic exam: Your provider will perform a pelvic exam to check for structural problems or signs of disease.
- Blood test: A blood test can check hormone levels to see if hormonal imbalance is a factor or if you are ovulating.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Your provider inserts an ultrasound into your vagina to look for issues with your reproductive system.
- X-ray hysterosalpingogram (HSG): X-rays capture an injectable dye as it travels through your fallopian tubes. This test looks for blockages.
Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or underweight can keep you from releasing eggs and having a regular menstrual cycle.
- Get enough sleep: Working in the night shift all the time might affect hormone levels, which can add to fertile issues. Try to get enough sleep.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins.
- Avoid harmful habits: Quit smoking to improve overall reproductive health. Limit alcohol intake, as excessive consumption may impact fertility.
- Stress management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga or mindfulness. Seek counselling or support if stress levels are impacting mental well-being.
- Regular check-ups: Schedule routine gynaecological check-ups for proactive monitoring of reproductive health and address any suspected hormonal imbalance or menstrual irregularities promptly.
- Prompt medical attention: Seek medical advice promptly if experiencing irregular menstrual cycle or related symptoms.
Treatment options:
Your doctor will decide the treatment protocol based on the specific problem, stage, history and overall health condition:
- Medications: Fertility medicine stimulates your ovaries to ovulate more eggs, which increases your chance of getting pregnant.
- Surgery: Surgery can open blocked fallopian tubes and remove polyps, fibroids or scar tissue.
- Other solutions: for infertility, include IVF treatment, freezing of eggs and Surrogacy
 Back
Back