
Why Women's Health is Important
Introduction to Women’s Health
Women comprise half of the global population and hold a unique and indispensable role in shaping their families and society. Not only do they shoulder responsibilities at home as mothers, wives, daughters and sisters, but they also contribute significantly to the global workforce.
The woman of the house is often the primary caregiver to the very young and the elderly. While playing all these roles and carrying multiple responsibilities, women often overlook their own health and well-being.

Prioritising women's health is crucial not only for women but for society at large be it reproductive health and maternal care to addressing specific diseases such as certain cancers and nutritional deficiencies that affect women in particular.
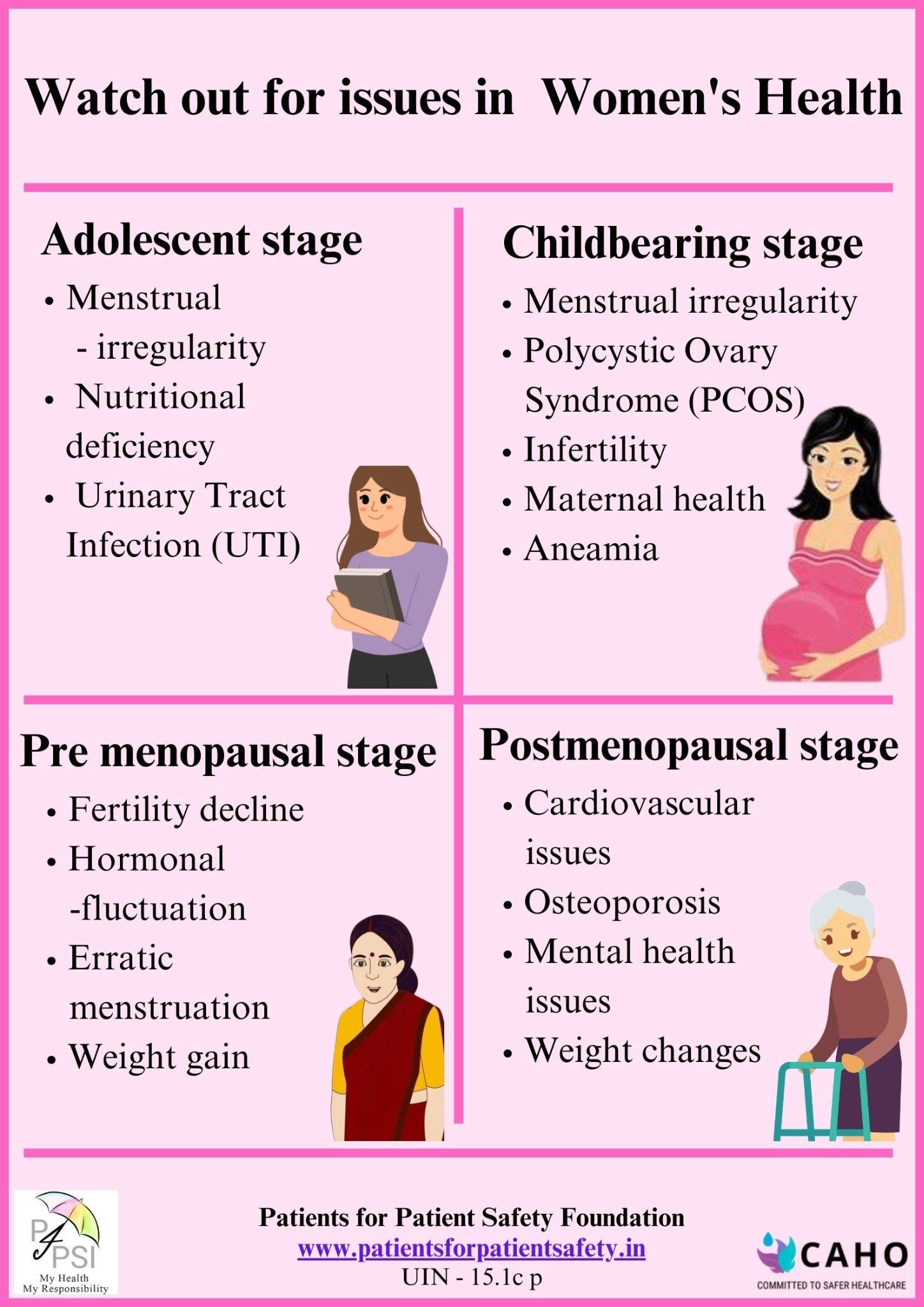
Issues at different stages of life
Different issues arise at different stages due to physiological changes in the body and hence need care and attention from the early years.
- Adolescence : Menstrual irregularities, nutritional deficiency, Urinary Tract Infections
- Childbearing stage : Infertility, menstrual problems and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Pre-menopausal stage : Bone health, fertility decline, hormonal fluctuations,
- Post-menopausal stage: Chronic conditions and cardiovascular issues
Common Health Issues in Women:
1) Reproductive and Maternal Health:
and postpartum period. If reproductive health is not adequately addressed, Women may face higher risks of maternal mortality and complications during childbirth. Ensuring good reproductive and maternal health involves providing access to appropriate education, medical care and support services.
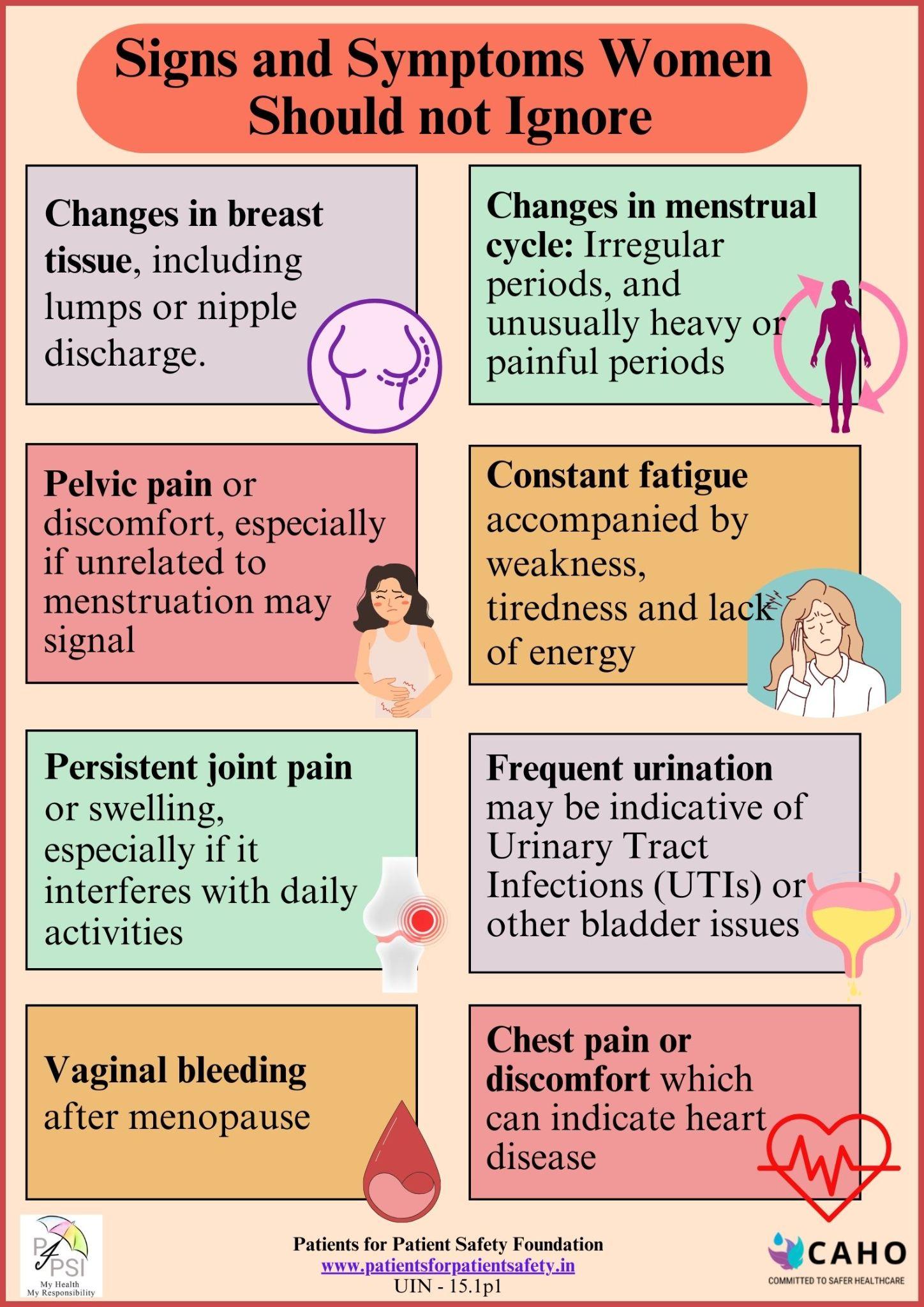
Menstrual Health is a critical component of women's overall health Related to their menstrual cycle. These include irregular and painful periods, heavy bleeding or subnormal, and other menstrual disorders such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and fibroids. Addressing menstrual health problems involves medical and gynaecologist evaluation and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and promote better reproductive health.
Read More: Menstrual cycle, what's normal, what's not
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) happens when a cysts develops in the ovaries which causes hormone imbalances. Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, light or heavy bleeding, thinning of hair, darkening of the skin and menstrual cramps. These symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life, affecting daily activities and emotional well-being. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes, along with medical interventions are effective in dealing with these issues.
Read More: PCOS - Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Fertilityproblems include difficulties or challenges that women may encounter when trying to conceive. Factors that adversely affect fertility include certain lifestyles such as excess smoking, alcohol intake, genetics, comorbidities and other environmental factors. Embracing a healthy lifestyle not only promotes overall well-being but also serves as a measure to optimise fertility. In case of infertility, other solutions include IVF treatment, freezing of eggs and Surrogacy can be an option.
Read More: Female Fertility: Symptoms, Detection & Prevention
Pre and Postnatal care during pregnancy, and after childbirth is essential for promoting the overall health and well-being of both the mother and child, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring a smooth transition into parenthood. Proper extra nutrition proper rest rest, sleep and emotional care during this period have a long-term impact on both the child’s and the mother’s health.
Read More: Postnatal Care
Hysterectomy may be recommended as a solution for treating conditions like uterine cancer, persistent pelvic pain, excess bleeding PCOS and or certain reproductive health issues. It is a surgical procedure involving the removal of the uterus. After surgery, during the recovery period, patients typically experience discomfort, fatigue, pain and need to restricted their normal activity levels. It is important for patients to follow post-operative care instructions carefully, including medication, rest, wound care, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Read More: Hysterectomy: Benefits, and Considerations
2) Nutritional Deficiency:
Nutritional deficiencies in women are a significant health concern, impacting reproductive health, and quality of life. These deficiencies occur when the intake or absorption of essential nutrients is inadequate to meet the body's needs. Women, due to various physiological factors such as menstruation, pregnancy, lactation, and menopause, are particularly vulnerable to certain nutrient deficiencies.
Anaemia is a prevalent health concern that affects women more, particularly during pregnancy, menstruation and menopause. This condition is characterized by efficiency in red blood cells or haemoglobin and represents inadequate levels of iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid. The optimal haemoglobin levels are different for men and women. For men, a normal level ranges between 14.0 grams per deciliter (gm/dL) and 17.5 gm/dL. For women, a normal level ranges between 12.3 gm/dL and 15.3 gm/dL. Regular monitoring and maintaining these levels are crucial for overall health. Common signs include tiredness, headache, weakness, yellow pale skin, and shortness of breath. Early detection, improved diets medical supplements advice by doctors can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected by anaemia.
Read More: Anaemia in Women
Osteoporosis characterised by weakened bones results from insufficient intake of Calcium and Vitamin D. This can lead to a decrease in bone strength that increases the risk of fractures (broken bones). Other symptoms include back pain, change in natural posture, and shortness of breath. It is a silent disease because you may not know you have this condition until you break a bone including the hips, wrist or spine. Prioritizing bone health through regular screenings, exercise vitamin supplements as prescribed by the doctor, and adopting a bone-friendly lifestyle can mitigate the impact of osteoporosis.
Read More: Osteoporosis - Prevention, Symptoms, Test & Treatment
3) Women Specific Cancers:
Women-specific cancers refer to malignancies that commonly affect the female reproductive system and other organs unique to women. These cancers include breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer, Each type of cancer has distinct risk factors, symptoms, and treatment including surgery, radiation Chemotherapy, long-term medication and lifestyle changes. Please seek immediate treatment from your Physician, Gynecologic and Oncologists
Breast cancer which is the most common globally, typically originates in the breast tissues. It can be identified as lump thickening or swelling in the breast or underarm, changes in the size or shape of the breast, nipple inversion and changes in skin texture. If left untreated, the tumours can metastasise leading to complex treatments that could be fatal. Early detection and intervention can ensure high recovery and survival rates.
Cervical cancer originates in the lower uterus and is caused by persistent high-risk HPV infection, and ranks fourth among cancers in women. Symptoms include bleeding between periods or abnormal periods, heavier or longer periods, watery vaginal discharge and pelvic pain or pain during intercourse. Even if a woman has HPV she may or may not get cervical cancer. Early detection and treatment greatly improve survival rates. Educating women about the importance of regular screenings and HPV vaccination is vital in the fight against cervical cancer.
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, which are a part of the female reproductive system. Many times symptoms such as Abdominal bloating or swelling, discomfort in the pelvic area, fatigue, and back pain, are overlooked or can be confused with indigestion. This is a and is silent can as it is designed in advanced stages making it more dangerous However, if detected early the chances of survival are far higher
Read More: Ovarian Cancer
4) Emotional and Mental Well-Being:
Mental health issues: Women are more prone than men to experience anxiety and depression as stress from work, career demands, domestic responsibilities and social expectations can be tough to handle. Seeking support from friends, family or mental health professionals can make a significant difference in managing mental health challenges.
Read More: Women & Mental Health
 Back
Back